Scope Tab¶
The Scope is a powerful time domain and frequency domain measurement tool as introduced in Unique Set of Analysis Tools and is available on all SHFLI instruments.
Features¶
- Two input channels
- 14 bit nominal resolution
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT): up to 2 GHz span (800 MHz in baseband), spectral density and power conversion, choice of window functions
Description¶
The Scope tab serves as the graphical display for time domain data. Whenever the tab is closed or an additional one of the same type is needed, clicking the following icon will open a new instance of the tab.
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Displays shots of data samples in time and frequency domain (FFT) representation. |
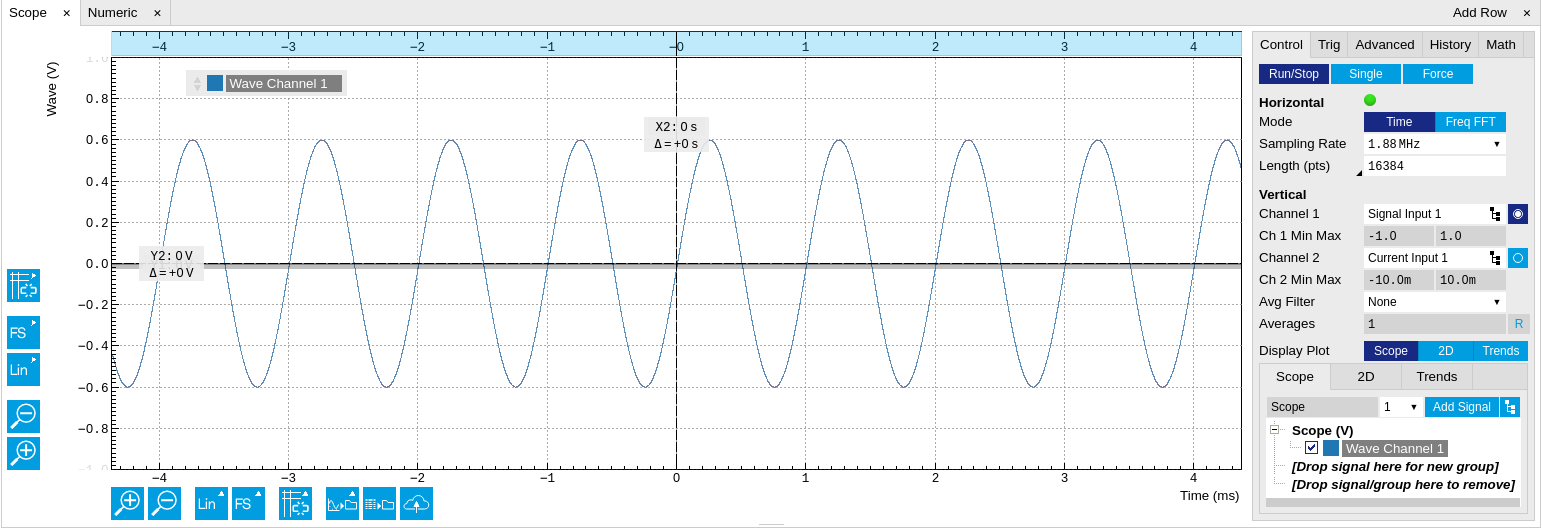
The Scope tab consists of a plot section on the left and a configuration section on the right. The configuration section is further divided into a number of sub-tabs. It gives access to a single-channel oscilloscope that can be used to monitor a choice of signals in the time or frequency domain. Hence the X axis of the plot area is time (for time domain display, Figure 1) or frequency (for frequency domain display, Figure 3). It is possible to display the time trace and the associated FFT simultaneously by opening a second instance of the Scope tab.
The Scope records data from a single channel at up to 2 GSa/s. The channel can be selected among the two Signal Inputs. The Scope records data sets of up to 64'000 samples.
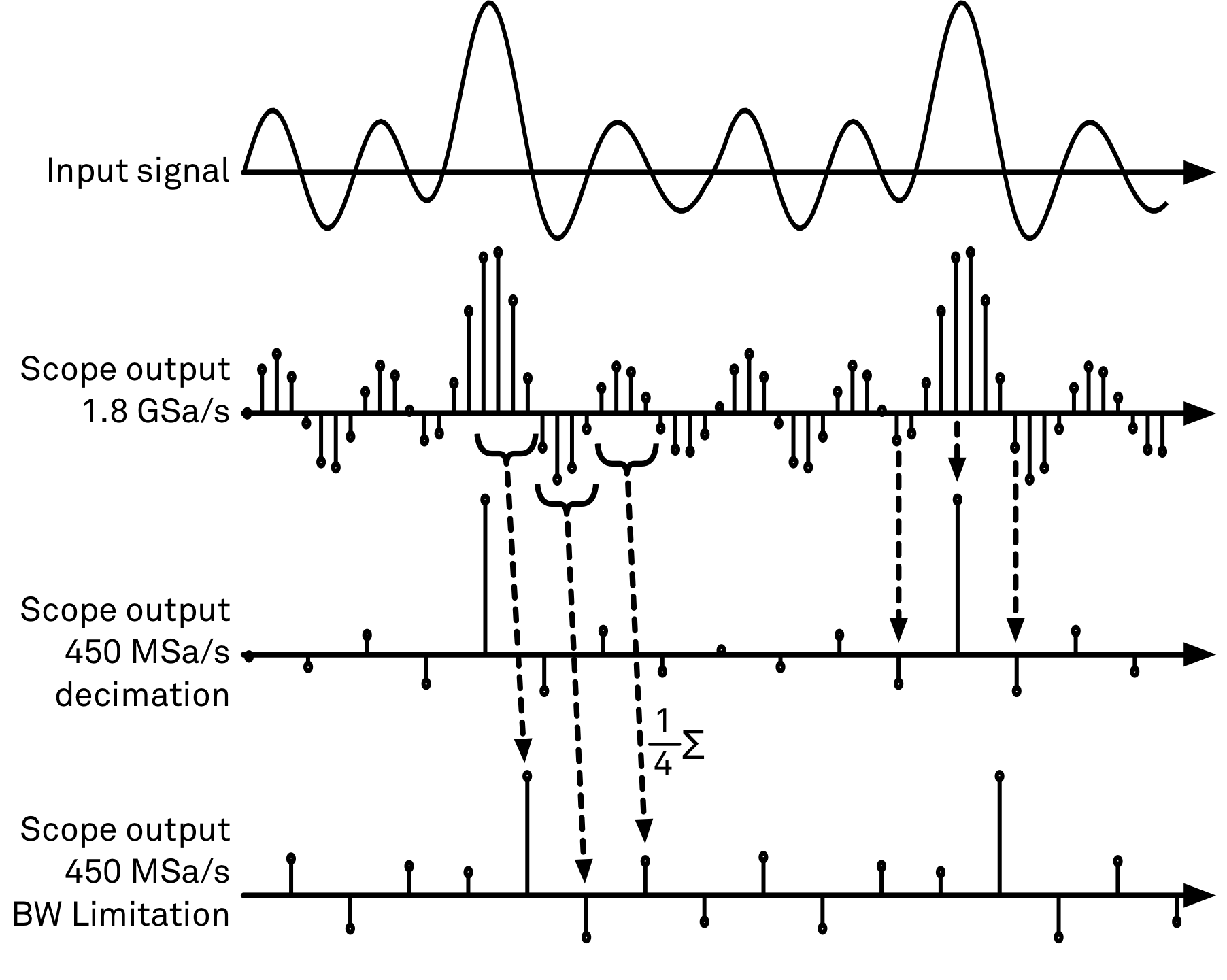
The product of the inverse sampling rate and the number of acquired points (Length) determines the total recording time for each shot. Hence, longer time intervals can be captured by reducing the sampling rate. The Scope can perform sampling rate reduction either using decimation or BW Limitation as illustrated in Figure 2. BW Limitation is activated by default, but it can be deactivated in the Advanced sub-tab. The figure shows an example of an input signal at the top, followed by the Scope output when the highest sample rate of 2 GSa/s is used. The next signal shows the Scope output when a rate reduction by a factor of 4 (i.e. 500 MSa/s) is configured and the rate reduction method of decimation is used. For decimation, a rate reduction by a factor of N is performed by only keeping every Nth sample and discarding the rest. The advantage of this method is its simplicity, but the disadvantage is that the signal is undersampled because the input filter bandwidth of the SHFLI instrument is fixed at 1 GHz. As a consequence, the Nyquist sampling criterion is no longer satisfied and aliasing effects may be observed. The default rate reduction mechanism of BW Limitation is illustrated by the lowermost signal in the figure. BW Limitation means that for a rate reduction by a factor of N, each sample produced by the Scope is computed as the average of N samples acquired at the maximum sampling rate. The effective signal bandwidth is thereby reduced and aliasing effects are largely suppressed. As can be seen from the figure, with a rate reduction by a factor of 4, every output sample is simply computed as the average of 4 consecutive samples acquired at 2 GSa/s.
Important
When operating in RF mode, the SHFLI’s Scope shows two traces per channel in the time domain, labeled I and Q. This is because it visualizes the data coming from the frequency mixing stage, which is composed of an in-phase and a quadrature component, similar to the data from the demodulators. In the frequency domain, this corresponds to a spectrum with symmetrical positive and negative frequencies centered around the channel’s center frequency.
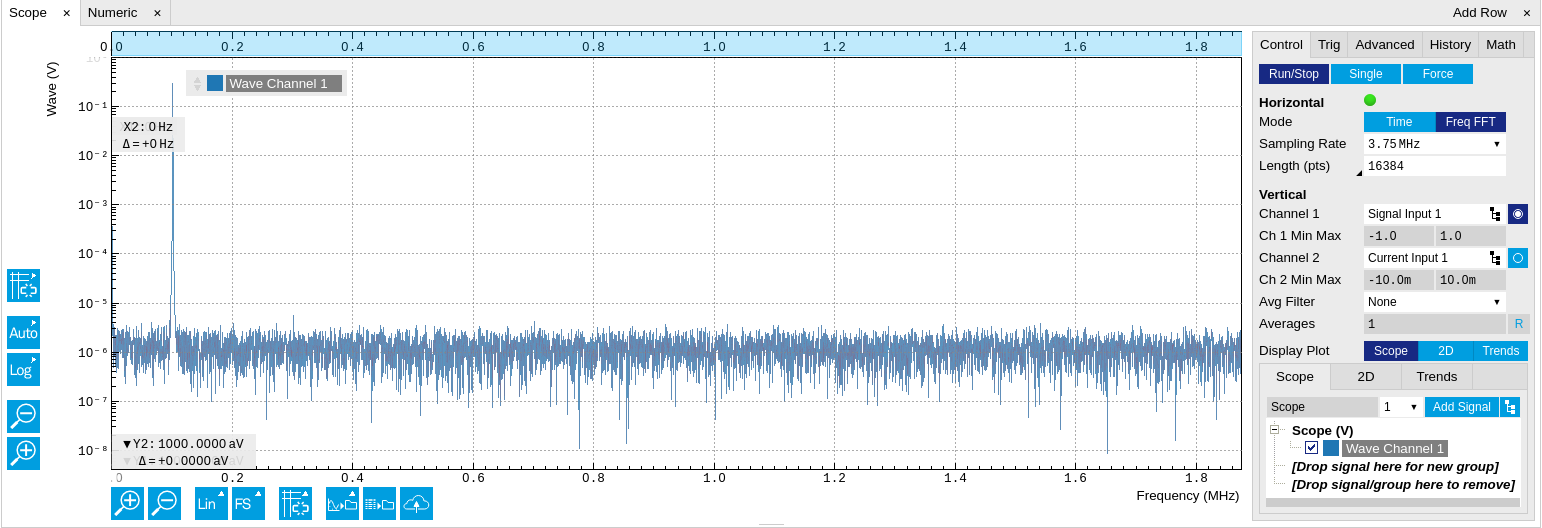
The frequency domain representation is activated in the Control sub-tab by selecting Freq Domain FFT as the Horizontal Mode. It allows the user to observe the spectrum of the acquired shots of samples. All controls and settings are shared between the time domain and frequency domain representations.
The Scope supports averaging over multiple shots. The functionality is implemented by means of an exponential moving average filter with configurable filter depth. Averaging helps to suppress noise components that are uncorrelated with the main signal. It is particularly useful in combination with the Frequency Domain FFT mode where it can help to reveal harmonic signals and disturbances that might otherwise be hidden below the noise floor.
The Trigger sub-tab offers all the controls necessary for triggering on different signal sources. When the trigger is enabled, then oscilloscope shots are acquired whenever the trigger conditions are met. Trigger and Hysteresis levels can be indicated graphically in the plot. A disabled trigger is equivalent to continuous oscilloscope shot acquisition.
Functional Elements¶
For the Vertical Axis Groups, please see the table "Vertical Axis Groups description" in the section called "Vertical Axis Groups".
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | ON / OFF | When triggering is enabled scope data are acquired every time the defined trigger condition is met. If disabled, scope shots are acquired continuously. |
| Segments | 1 to 32768 | Specifies the number of segments to be recorded in device memory. The maximum scope shot size is given by the available memory divided by the number of segments. This functionality requires the DIG option. |
| Shown Trigger | integer value | Displays the number of triggered events since last start. |
| Control/Tool | Option/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FFT Window | Cosine squared (ring-down) | Several different FFT windows to choose from. Each window function results in a different trade-off between amplitude accuracy and spectral leakage. Please check the literature to find the window function that best suits your needs. |
| Rectangular | ||
| Hann | ||
| Hamming | ||
| Blackman Harris | ||
| Flat Top | ||
| Exponential (ring-down) | ||
| Cosine (ring-down) | ||
| Resolution (Hz) | mHz to Hz | Spectral resolution defined by the reciprocal acquisition time (sample rate, number of samples recorded). |
| Correction | ON / OFF | When Power is selected, it applies power correction to the spectrum to compensate for the shift that the window function causes. Power correction is useful for noise measurements to correct the noise floor. When Amp is selected, amplitude compensation is applied which corrects the peak amplitudes of coherent tones. |
| Absolute Frequency | ON / OFF | Shifts x-axis labeling to show the absolute frequency in the center as opposed to 0 Hz, when turned off. |
| Spectral Density | ON / OFF | Calculate and show the spectral density. If power is enabled the power spectral density value is calculated. The spectral density is used to analyze noise. |
| Power | ON / OFF | Calculate and show the power value. To extract power spectral density (PSD) this button should be enabled together with Spectral Density. |
| Persistence | ON / OFF | Keeps previous scope shots in the display. The color scheme visualizes the number of occurrences at certain positions in time and amplitude by a multi-color scheme. |
| Rate | Streaming rate of the scope channels. The streaming rate can be adjusted independent from the scope sampling rate. The maximum rate depends on the interface used for transfer. Note: scope streaming requires the DIG option. |
For the Math sub-tab please see the table "Plot math description" in the section called "Cursors and Math".





